Topology¶
Generic concepts and components¶
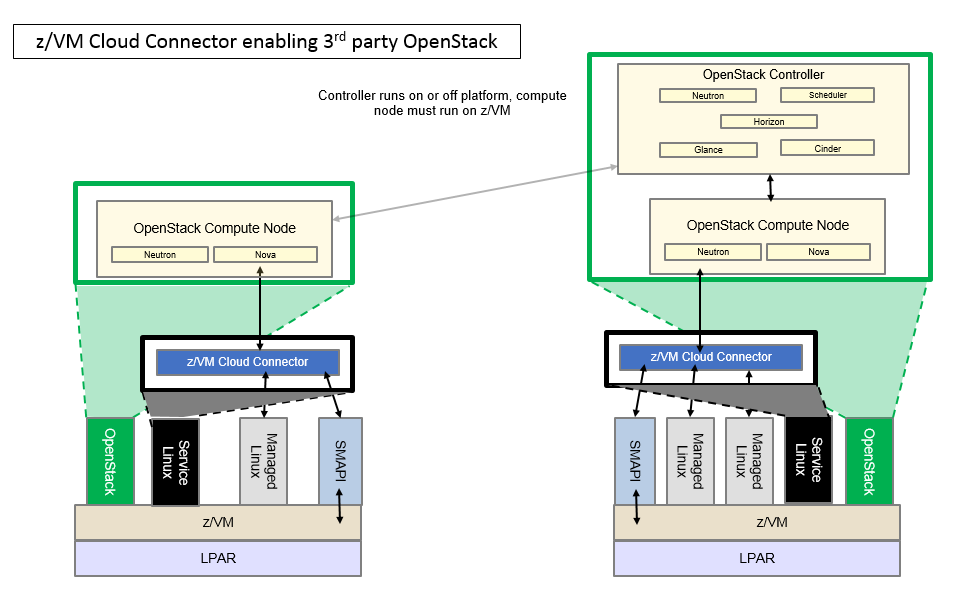
Following picture shows a conceptual view of the relationship between any OpenStack solution and z/VM.
An OpenStack solution is free to run its components wherever it wishes; its options range from running all components on z/VM, to running some on z/VM and others elsewhere, to running all components on other platform(s). The solution is also free to source its components wherever it wishes, either using z/VM. OpenStack enablement components or not.
z/VM ships a set of servers that provide local system management APIs. These servers consist of request servers that accept local connections, receive the data, and then call one of a set of worker servers to process the request. These servers are known collectively as SMAPI. The worker servers can interact with the z/VM hypervisor (CP) or with a directory manager. A directory manager is required for this environment.
Overall architecture¶
z/VM openstack enablement rely on z/VM cloud connector, the compute service (nova-compute) can either run on remote server other than z/VM itself or run on top of virtual server which hosted on z/VM.
Function Call flow¶
Following is a picture describe the call routine of spawn function, openstack zvm driver managed zvm through REST API call provided by zvm cloud connector.
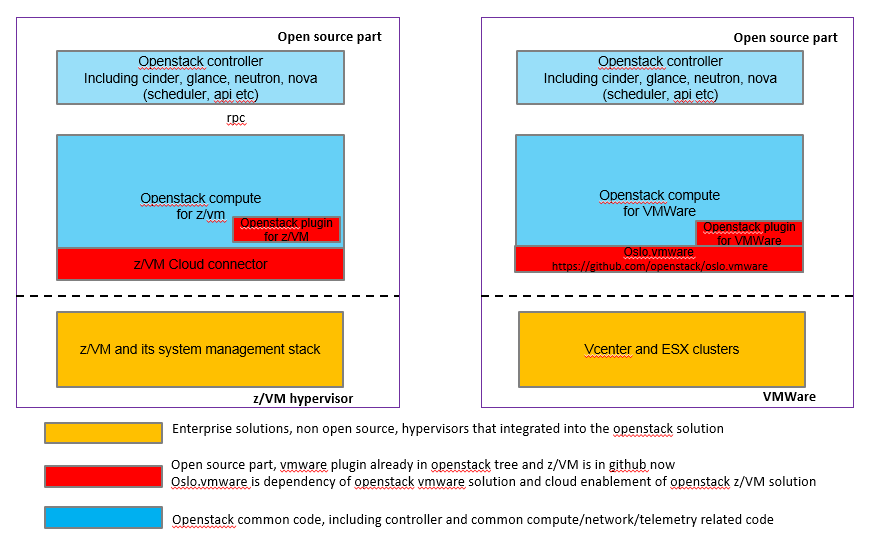
Compare with vmware openstack driver¶
Here’s architecture comparsion between z/VM and vmware enablement for openstack.